 Age
Age
 Family history
Family history
 Lifestyle
Lifestyle
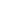 Androgen levels
Androgen levels
 Environmental factors
Environmental factors
close to 100%
Early-stage (stage I)close to 80%
Mid-stage (stage II-III)30% to 40%
Late-stage (stage IV.)1
Urethral symptoms: frequent urination (especially at night), urgency, tingling or burning sensation in the urethra, difficulty in urinating, and a weakened or interrupted urine stream.2
Problems with urination: the urine stream may become weak or irregular, and sometimes there may be a sensation of dribbling urine remaining.3
Urethral strictures: there may be difficulty in passing urine or the sensation that urine flow is obstructed.4
Sexual function problems: including erectile dysfunction, difficulty ejaculating, pain or discomfort.5
Other signs: include low back pain (if the cancer has spread to nearby bones), anemia (due to potentially hidden bleeding), and swollen lymph nodes.
Traditional Treatment
Integrated Minimally Invasive Treatment x St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou
1、No need for resection, high surgical precision, and fewer complications: minimally invasive treatment can preserve the kidney and its functions to a great extent, and enter the body through tiny incisions to carry out high-precision therapeutic operations, which greatly reduces postoperative infections and other complications.Traditional treatment for prostate cancer
Surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, etc.
Interventional Therapy
local precise drug infusion delivers a drug concentration 2-92 times higher than systemic chemotherapy, resulting in less trauma and fewer side effects.

Cryotherapy
Using a 2mm cryoprobe, tumors can be efficiently ablated in ten minutes after undergoing 2 cycles of cooling and rewarming.
Combined Knife
Switching between extremely low and high temperatures to efficiently ablate tumors. Especially, applies to large tumors and elderly, frail cancer patients.
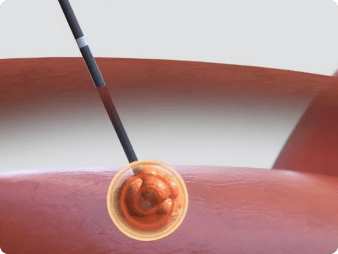
Microwave ablation
Microwave ablation boasts high thermal efficiency and can eradicate tumors less than 5 cm in diameter in a single session.
 Smoking
Smoking
 Age
Age
 Obesity and hypertension
Obesity and hypertension
 Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease
 Genetic factors
Genetic factors
75%-95%
Early-stage (stage I)40%-70%
Mid-stage (stage II-III)< 30%
Late-stage (stage IV.):
Traditional Treatment
Integrated Minimally Invasive Treatment x St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou
1、No need for resection, high surgical precision, and fewer complications:minimally invasive treatment can preserve the kidney and its functions to a great extent, and enter the body through tiny incisions to carry out high-precision therapeutic operations, which greatly reduces postoperative infections and other complications.Traditional treatment for kidney cancer
Surgical, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, etc.

Interventional treatment
local precise drug infusion delivers a drug concentration 2-92 times higher than systemic chemotherapy, resulting in less trauma and fewer side effects.

Cryotherapy
Using a 2mm cryoprobe, tumors can be efficiently ablated in ten minutes after undergoing 2 cycles of cooling and rewarming.

Combined Knife
Switching between extremely low and high temperatures to efficiently ablate tumors. Especially, applies to large tumors and elderly, frail cancer patients.

Microwave ablation
Microwave ablation boasts high thermal efficiency and can eradicate tumors less than 5 cm in diameter in a single session.
 Smoking
Smoking
 Occupational Exposure
Occupational Exposure
 Age
Age
 Genetic factors
Genetic factors
 Other chronic bladder conditions
Other chronic bladder conditions
 Lifestyle habits
Lifestyle habits
60%-90%
Early-stage (stage I)30%-50%
Mid-stage (stage II-III)<30%
Late-stage (stage IV.)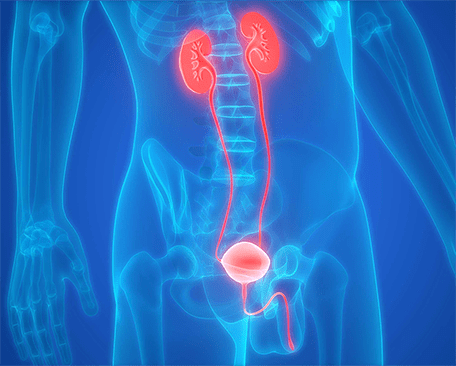
Traditional Treatment
Integrated Minimally Invasive Treatment x St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou
1、No need for resection, high surgical precision, and fewer complications:minimally invasive treatment can preserve the bladder and its functions to a great extent, and enter the body through tiny incisions to carry out high-precision therapeutic operations, which greatly reduces postoperative infections and other complications.Traditional treatment for bladder cancer
Surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, etc.

Interventional treatment
local precise drug infusion delivers a drug concentration 2-92 times higher than systemic chemotherapy, resulting in less trauma and fewer side effects.

Cryotherapy
Using a 2mm cryoprobe, tumors can be efficiently ablated in ten minutes after undergoing 2 cycles of cooling and rewarming.

Combined Knife
Switching between extremely low and high temperatures to efficiently ablate tumors. Especially, applies to large tumors and elderly, frail cancer patients.
Particle Knife
Initially, the suitable radiation energy and particle dose are determined based on the tumor's characteristics, size, and location. Subsequently, guided by imaging equipment, 125 iodine particles are implanted into the tumor or the tissue affected by tumor infiltration.