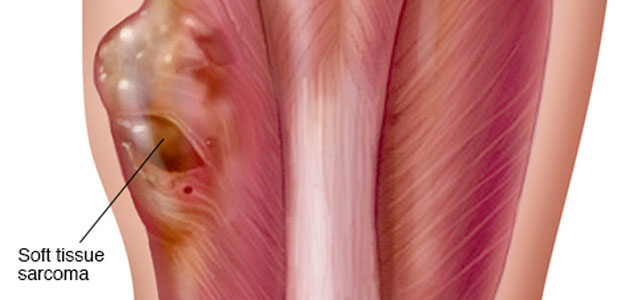
What is soft tissue cancer?
All malignant tumors that originate in the fiber, fat, smooth muscle, striated muscle, synovial membrane, blood vessel, lymphatic vessel and locate in soft tissues (with the exception of visceral organs), are called as soft tissue cancers or soft tissue sarcomas as well. Sarcoma can occur in the soft tissues throughout the body, especially in the limbs, trunk, retroperitoneal part and pate; among these, the limbs are mostly seen, about 60% in all cases. The incidence rate of soft tissue cancer is approximately 2/100,000 to 3/100,000, which amounts for 1% among adult’s malignant tumors, but it has no sexual orientation. Generally the elderly have a higher prevalence. Soft tissue cancer is very easy to spread to the surrounding normal tissue and its fatality rate is 2%.
Survival rate of soft tissue cancer
Prognosis of soft tissue cancer patients is better than that of epithelium tumor patients and its 5-year survival rate is about 50%. Prognosis mainly depends on tumor’s condition and invasion severity of adjacent organs, and the prognosis of limbs is prior to other parts. For patients who have occurred metastasis but treatments still can control the condition, the survival rate for most of these patients after being diagnosed with metastasis is about 1 year.
If you're diagnosed with cancer, please consult online doctors for more information.
Causes of soft tissue cancer:
Currently, causes of soft tissue cancer have not been defined yet, but it is well-known that the causes of soft tissue cancer are not single.
Congenital malformation: angeioma is commonly seen among infants and children. The vast majority of such lesions are found after birth. As children grow, vascular lesions will grow correspondingly and proportionally and never fade away without rapid growth history.
Familial heredity: many studies show that many tumor cells manifest chromosomal abnormalities. People who have chromosomal abnormalities would own higher incidence rate than that of normal people, and also have the characteristic of familial heredity.
Foreign substance stimulation: according to animal experiment and clinical observation, long term of foreign substance stimulation on the body may induce soft tissue cancer.
Chemical materials stimulation: an epidemiological survey has discovered that workers who are long-term exposed to polyvinyl chloride have high risk of suffering from angiosarcoma of the liver
Trauma: a considerable portion of soft tissue cancer patients have clear trauma history on the site of tumor.
If you're diagnosed with cancer, please consult online doctors for more information.
Symptoms of soft tissue cancer:
The most common symptoms are painless swelling or mass. Sometimes, the invaded bone or joint may feel pain, especially during the night. Besides, there are some ordinary and very rare symptoms like getting a fever, general malaise, weight loss or bleeding and so on.
Harm of soft tissue cancer
Soft tissue cancer usually grows rapidly with huge volume, invades and damages surrounding normal tissues. The tumor itself may have necrosis, bleeding and secondary infection, and often spreads to the lung, bone, skin, brain, adrenal, pancreas and other organs by hematogenous dissemination. Patients often die of cachexia, severe bleeding or widespread metastasis.
How to diagnose?
Chemical examination
Blood tests: checking biochemical indicator of blood serum, LDH, protein, electrolyte, calcium, acidity and alkaline phosphatase level, is helpful for distinguished diagnosis;
Imaging examinations:
X-ray photographs examination: X-ray photographs are helpful for further getting to know the scope of soft tissue tumor, transparency and its relationship with adjacent bones;
CT or MRI examination: the scan can search the mass of soft tissue sarcoma and define its sizes and relationship with surrounding structures;
Ultrasonic imaging examination: This examination can check the tumor volume range, envelope boundary and echoes inside tumor tissue of tumor body so as to distinguish whether it is benign or malignant;
Bone scan can provide more information regarding to type of sarcoma and its scope;
Arteriography examination: it can indicate the rough margins of tumor.
Pathologic examinations:
Cytological examination:
①for soft tissue tumors that have broken, use smear or scraper acquisition method to obtain cells and then conduct microscopic examination for confirmation;
②for the chest ascites caused by soft tissue sarcoma, it must use just-obtained fresh specimens for immediate centrifugal sedimentation; then absorb deposits for smear;
③smear examination is suitable for relatively big and deep tumors that are ready for radiotherapy or chemotherapy, or for lesions that have spread or reoccurred.
Biopsy: biopsy is necessary for suspected lesions, but the choice of biopsy methods should be taken into consideration for possible surgery to be performed. Surgical operation may be performed at the same time when conducting biopsy or may be preceded by biopsy.
If you're diagnosed with cancer, please consult online doctors for more information.
Staging of soft tissue cancer
Tumor staging depends on the size of the tumor, pathological grading and whether there is a nearby lymph nodes metastasis or distant metastasis. Soft tissue cancer of adults shall be divided into 4 stages: Stage I, II, III means there is no nearby lymph nodes metastasis or distant metastasis. During Stage IV, if there is regional lymph nodes metastasis, then it is Stage IVa; if there is distant metastasis, then it is Stage IVb. Pathological grading mainly depends on tumorous mitotic values.
The first grading: division of tumor cells is slow and metastases seldom occur;
the second grading: tumor cells have moderately differentiated with the probability of metastasis being less than 20%;
the third grading: division of tumor cells is relatively quick with the probability of metastasis being exceeding 50%.
5-year survival rate for people with low differentiated tumor usually exceeds 75%; while for people with high differentiated tumor, it is less than 25%.
Treatment methods of soft tissue cancer:
radical operation: It is to cut the tumor and its surrounding tissue to certain width;
debulking operation: It is targeted at some soft tissue cancers that cannot be cut completely. After the surgery, other non-surgery treatments can be performed to improve patients’ life quality and prolong their life span.
amputation: It is suitable for patients of advanced stage with big tumor, accompanied by a variety of serious symptom.
Radiotherapy: it is applied to prevent local recurrence of tumor that is sensitive to rays. It can be performed prior to or after surgery.
Chemotherapy: it kills tumor through drugs. In order to ensure good therapeutic effect, the dosage of drugs is relatively large and the drugs also cause many side effects.
If you're diagnosed with cancer, please consult online doctors for more information.