 |
What is lymphoma?
Lymphoma is a malignant tumor originating from the lymphohematopoietic system, which mainly manifests as painless lymph node enlargement, hepatosplenomegaly, and all tissues and organs of the body can be involved, accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever, night sweats, emaciation, and itching. According to WHO statistics, the global incidence of lymphoma is about 589,600 cases, and the global standardized incidence rate is about 6.6/100,000 cases.
Can middle and late-stage lymphoma be cured? Minimally invasive techniques with little side effects and trauma can help bladder cancer patients avoid surgical removal, avoid suffering from traditional radiotherapy, and effectively prolong survival.
For more knowledge about cancer, please click online doctors for consultation.




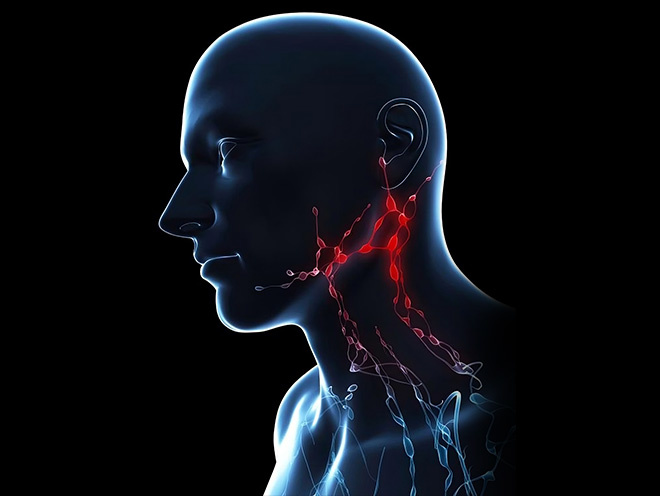
Lymphoma is a malignancy of immune system can develop in any part of body. It usually appears as a solid tumor in the organs rich in lymphatic tissues and tends to encroach on lymph nodes, tonsil, spleen and bone marrow. It is easily ignored because of insidious symptoms. But the survival rate can highly improved if its symptoms are noted in early stage and take treatments in time. Therefore, it is necessary for us to know some symptoms of lymphoma.
1、 The most typical symptoms of lymphoma are painless superficial lymph nodes, which grow gradually with smooth surface and in the hardness like nasal tip. Swelling lymph nodes are most commonly occurring in neck and supraclavicular regions, after that are in armpits and inguens. Some cases would mainly present the symptom of swelling lymph nodes deep in body, for example, swelling lymph nodes in mediastinum, abdominal cavity and pelvis. Those cases come with an insidious onset that when the patients are diagnosed lymphoma, the swelling lymph nodes deep in body normally are every obvious to note.
2、Progressive swelling lymph nodes may affect or press on tissues or organs around and cause correspondent symptoms. For example, when superior vena cava is pressed by the swelling lymph nodes in mediastinum would block blood backflow to cause swollen face and neck, chest distress, chest pain or difficult breath and so on. If the swelling lymph nodes of pelvis and abdominal cavity press on gastrointestinal tract, ureter or bile ducts etc. would lead to intestinal obstruction, hydronephrosis, jaundice, which may also come with abdominal pain and distention.
3、Expect lymphatic system, lymphoma can also encroach on other organs and present correspondent symptoms. For instance, gastrointestinal lymphoma would show the symptoms like abdominal pain, gastrointestinal ulcer, bleeding and oppression etc., which are same as stomach diseases and intestinal cancer do. Lymphocytoma cutis is normally mistaken as psoriasis, eczema and dermatitis. If the tumor develops in brain, headache, blurring vision, disturbance of speech, unconsciousness, and change in disposition, dyskinesia of limbs or whole body, and even paralysis in severe cases. When tumor invades bones can lead to pain or fracture of bones, and if in nasopharynx may develop symptoms like nose obstruction, running nose, nasal bleeding, which are similar to the ones of nasopharyngeal cancer.
4、Lymphoma is a general disease, except the above symptoms, fever, night sweat, acratia, emaciation, loss of appetite, rash, itching, anemia and other systematic symptoms may develop in more than 50% patients. From this, superficial lymphoma comes with obvious symptoms that are easy to find early. But for the lymphoma develops deep in body, it is difficult to note because concerning symptoms would occur when the tumor is large enough.
Specialist from St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou reminded that, some diseases may also present the symptoms mentioned above, a patient may not suffer from lymphoma once these symptoms occur and should go to hospital for examinations in time. Then if a patient is diagnosed lymphoma, timely treatments can perform to improve therapeutic effect and living quality.
For more knowledge about cancer, please click online doctors for consultation.
The diagnosis of lymphoma can not be worked out blindly, since clinical symptoms vary when lesion location and range change, and blind diagnosis will increase the misdiagnosis rate. And below are the examinations may help a patient diagnose lymphoma.
1. Imaging examination
1)X-ray is to observe the lymph nodes of lung hilum, midiastinum, carina tracheae and endosperm, while it can observe if any infiltration in lung hilum occurs. The obvious swelling lymph nodes in anterosuperior mediastinum and lung hilum may indicate the sign of malignancy, but before that the swelling lymph nodes arising from extrapulmonary tuberculosis, fungous infection or other cancers should be excluded. If a patient is suspected suffering from swelling lymph nodes in pelvis, retroperitoneum and paraaortic regions may have lower extremity lymphography for diagnosis.
2) Computerized tomography(CT). It can detect the lymph tissues which can not find through lower abdominal lymphadenography. Chest CT scan can help to diagnose mediastinal lesions and the lymph nodes closed to trachea, lung hilum and aortic clear space.
3)Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can reveal the structure of blood vessels and can have multidirectional and multi-plane scans inside body.
4) Radioisotopic scanning. Bone scans can find lesion early than X-ray. Bone scan can indicate the rising intake of nuclide in lesions. In addition, diffuse histocytic lymphoma normally would come with bone infiltration.
5)Ultrasound examination can detect the lymph nodes over 2cm dia., however, it cannot identify if the increased lymph node is causing from cancer infiltration or reactive hyperplasia or chronic inflammation. Besides, through it can find the splenohepatomegalia and the obvious nodules in liver or spleen.
Doctor would get some tissues from the tumor found in a lymphoma patient through imaging examinations for biopsy to confirm if the tumor is benign or malignant.
2. Biopsy
1) Biopsy of lymph nodes. Malignant lymphoma should be diagnosed through biopsy and pathological samples should mainly be lymph nodes.
2) Biopsy of bone marrow. The incidence for lymphoma encroaches on bone marrow can highly reach 40%~90%. Bone marrow biopsy can confirm if malignant lymphoma encroaches on bone marrow and it normally has to be performed through puncture.
3)Biopsy of liver. In Non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases, small lymph cells and small cleaved cells are more tending to encroach on liver.
4) Blood picture. The white blood cells of Hodgkin’s disease in most cases are within normal range while little patients appear mild or obvious increase of white blood cells. Besides that, a non-Hodgkin lymphoma patient would present abnormal increase of white blood cells and is accompanied by opposite or absolute increase of lymph cells.
St. Stamford Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou reminds that when swelling and other abnormality occur in body, the patient should go to hospital timely for examination and treatments, by which can effectively control the disease.
For more knowledge about cancer,please click online doctors for consultation.
Staging of lymphoma and 5-year survival rate (Statistics comes from American Cancer Society):
Prognosis of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma depends on the malignancy. Though lymphoma patients with low malignancy are not easy to be treated, 5-year survival rate can reach 70%. Lymphoma with high malignancy is highly invasive, thus the survival rate decreases as the stage goes up. About 30% to 40% lymphoma patients can maintain long-term survival after treatment.
For more knowledge about cancer, please click online doctors for consultation.